Editorial: Fatty Liver
Fatty Liver and Its Management: A Growing Health Concern
Ibrahim Masoodi
Consultant Gastroenterology
East Sussex NHS Trust Eastbourne England.
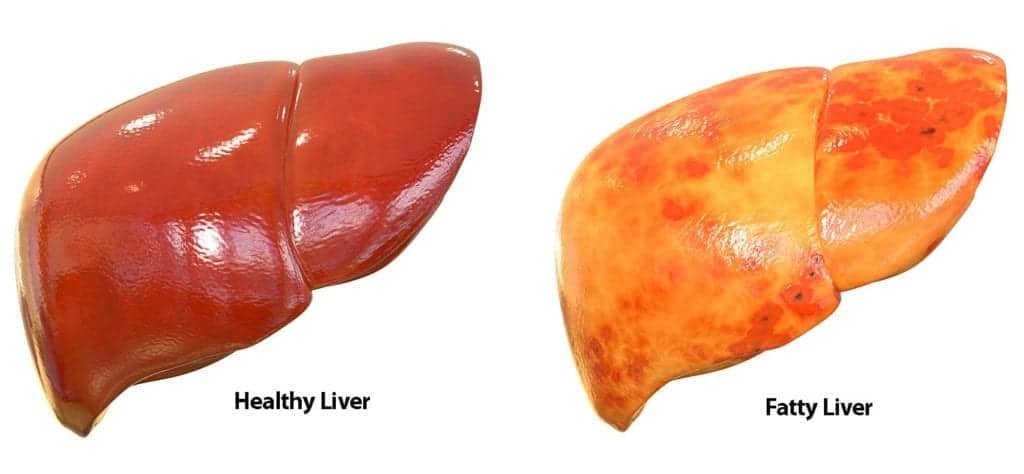
Fatty liver disease characterized by the excessive accumulation of fat in the liver has become a significant public health concern .Once considered a rare condition it is now one of the most common liver diseases worldwide .The two main types of fatty liver disease are alcoholic fatty liver disease AFLD caused by excessive alcohol consumption and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD which is linked to obesity insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome .The latter in particular is rapidly increasing in prevalence mirroring the global rise in obesity and diabetes.
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
While a mild accumulation of fat in the liver is typically harmless excessive fat can lead to inflammation and liver damage . NAFLD can progress to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis NASH which can cause liver fibrosis cirrhosis and even liver cancer .The insidious nature of NAFLD is particularly troubling because it is often asymptomatic until significant liver damage has occurred.
The Growing Epidemic
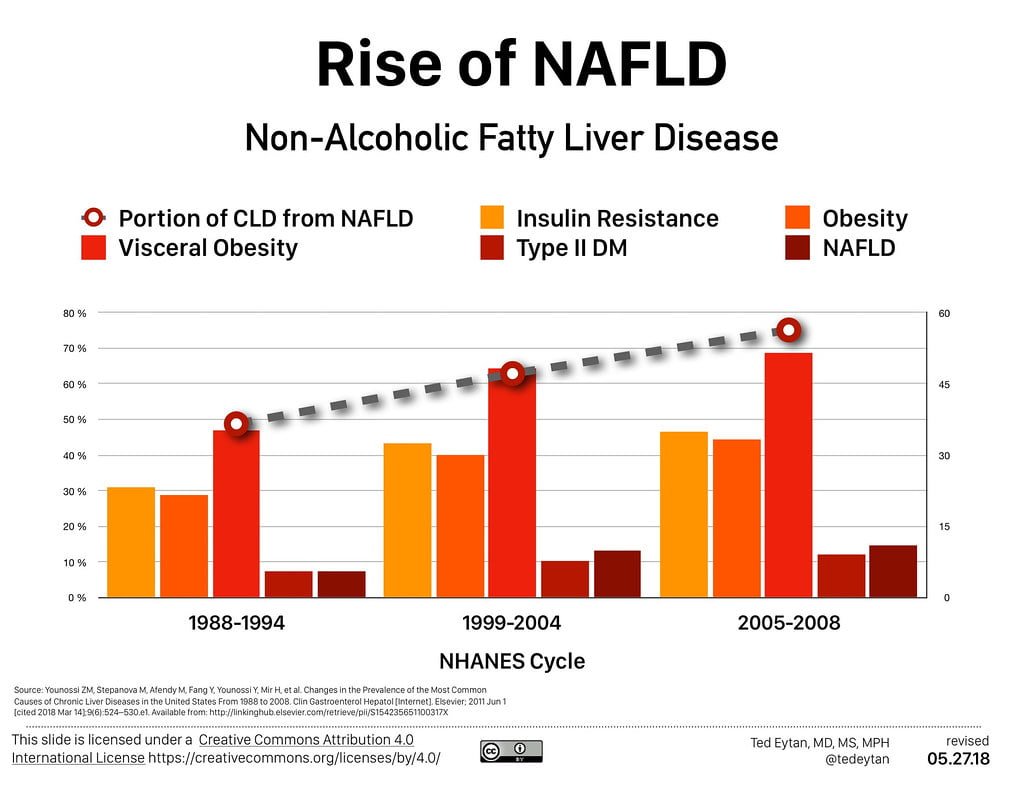
The global burden of NAFLD is staggering with estimates suggesting that up to a quarter of the worlds population may be affected .This rise is closely linked to lifestyle factors such as poor diet, physical inactivity and the increasing prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes across the globe. The condition is not confined to adults alarmingly it is also being diagnosed in children and adolescents at an increasing rate now.
Management Strategies
Effective management of fatty liver disease requires a multifaceted approach
- Lifestyle Modifications: The cornerstone of managing NAFLD and AFLD is lifestyle modification Weight loss achieved through a combination of dietary changes and increased physical activity can significantly reduce liver fat and improve liver function
- A diet rich in fruits vegetables whole grains and lean proteins while low in saturated fats refined sugars and processed foods is recommended
- Regular exercise, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate intensity activity per week, is also crucial
- Medical Interventions: While no medications are specifically approved for NAFLD,, several drugs are being investigated. For those with NASH certain diabetes medications vitamin E and newer agents targeting metabolic pathways show promise .
- For AFLD abstinence from alcohol is imperative In severe cases where lifestyle changes are insufficient, bariatric surgery may be considered for obese patients
- Regular Monitoring: Patients with fatty liver disease require regular monitoring to assess liver function and progression .This includes blood tests, imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI and Fibroscan .Sometimes liver biopsy to evaluate the extent of liver damage or any confounding illness.
- Addressing Comorbidities: Managing associated conditions such as diabetes ,hypertension and hyperlipidemia is essential
- Comprehensive care that addresses these comorbidities can improve overall outcomes and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, which is a major cause of mortality in NAFLD patients
Prevention and Public Health Initiatives
Preventing fatty liver disease necessitates public health initiatives that promote healthy lifestyles. Education campaigns to raise awareness about the risks of poor diet and sedentary behavior along with policies to reduce the consumption of sugary beverages and processed foods are critical
Schools and workplaces should be encouraged to provide environments that support healthy eating and physical activity
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease is a silent but significant threat to global health driven by the obesity epidemic and sedentary lifestyles .Addressing this condition requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications medical management regular monitoring and public health initiatives .As we continue to learn more about this disease it is imperative to implement strategies that can mitigate its impact and improve the health and wellbeing of affected individuals The time to act is now for the health of our livers is inextricably linked to our overall health. Weight reduction and exercise are the only measures to prevent progression of fatty liver to Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis which marks the onset of liver damage in a patient with fatty liver.
Join the mailing list!
Get the latest articles delivered right to your inbox!
